Switches: Markings, Types, and Safety Considerations
Posted on 7/15/19 7:57 AM

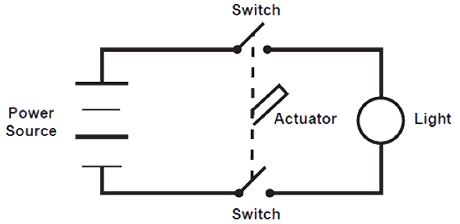
From being used on a vacuum cleaner to being used on a life-support machine, the purpose of a switch is to open and close a circuit. A switch is used when incoming power in an electrical product design needs to be controlled. Opening a circuit (turning a device OFF) is achieved by breaking the connection. This interrupts the current flow. Closing the circuit (turning a device ON) allows the current to flow again.
On/Off Markings
A common style of a switch is a rocker design, which includes on/off markings. To meet the standard IEC 60417, the symbol for ON is “I” (a straight line) and the symbol for OFF is “O” (a circle). It is important to check the appropriate equipment standard for instructions regarding the position of “on” as some may require the “I” to be installed in a vertical position.
These on/off markings can be found on the end of the actuator or on the face of it. The actuator is the mechanical component used to manually turn a circuit on and off. “From my experience, the face is the most common and easiest to see. They can either be ink or paint marked or the marks can be molded into the actuator. The molded-in marks are harder to see,” explained Dan Ford, Technical Support Specialist at Interpower.
Types of Switches
There are different types of switches to choose from. A switch wire or pole indicates the number of circuits that it controls. So a single-pole switch refers to one circuit and a double-pole switch refers to two circuits. A double-pole switch can be similar to two single-pole switches side-by-side.
There are four main classifications for the types of switches:
- Single-pole, single-throw (SPST)
- Single-pole, double-throw (SPDT)
- Double-pole, single-throw (DPST)
- Double-pole, double-throw (DPDT)
The double-pole, single-throw rocker design is used in switches carried by Interpower. DPST switches are commonly used in equipment. For example, this type of switch can be found in a home computer and a large piece of manufacturing equipment.
The main reason for choosing the DPST design is the safety consideration in worldwide markets, because many global wiring systems are generally non-electrically polarized. By using the double-pole, single-throw switch, the contacts can cut off power to both the line and neutral when flipped into the off position.
Additional Resources
For more information on switches offered by Interpower, see Switches and the Featured Product page.
Interpower offers free technical support. For further assistance, please see Interpower’s contact information below.
Topics: electrical safety, product design, switches